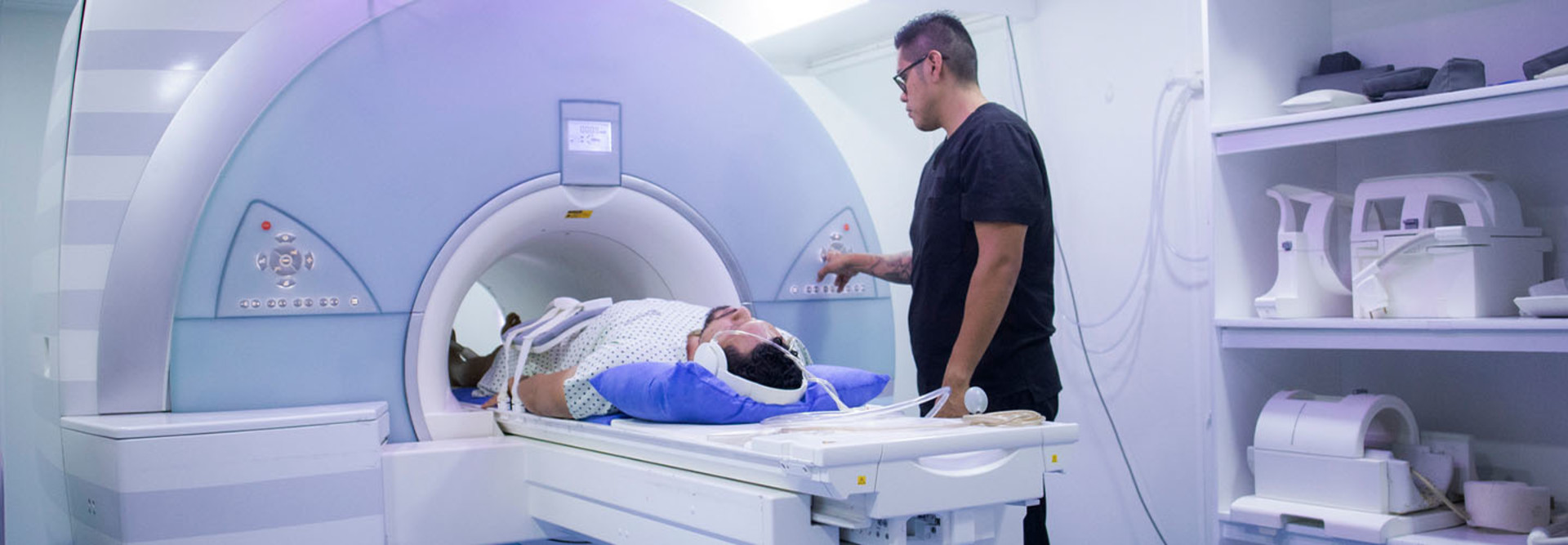
The MRI system integrates dynamic lighting, sound and video to encourage relaxation and positive distraction to ease patient stress during the procedure.
Patients can also have a more comfortable experience using special goggles. “Instead of staring at the interior of the scanner, which can feel claustrophobic, patients can watch a video projected on the wall in front of the scanner,” he says.
The video, accompanied by sound through headphones, creates a relaxing environment intended to reduce anxiety during the procedure. “Being able to offer this experience has led to improved patient satisfaction scores,” Hayashi says.
DISCOVER: Why are healthcare organizations launching innovation centers?
Virtual MRI Programs Expand Accessibility for Patients
Other healthcare providers are standing up programs to boost the reach of their MRI services. The Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC), for instance, has a virtual MRI program to improve patient access, taking a decentralized approach to make MRI services available in more locations across the communities it serves.
The program allows MRI technologists in Charleston, S.C., to remotely connect to MRI scanners at other locations and collaborate with onsite technologists.
Dr. Reginald Munden, chair of the radiology department at MUSC, describes the health system’s program as a “virtual cockpit,” enabling technologists to perform specialized scans such as cardiac MRIs, which require advanced expertise.
The virtual MRI system is equipped with cameras that allow technologists at different sites to see each other and monitor the patient in the scanner. This setup facilitates real-time consultation and communication between the remote and onsite teams, enabling collaborative operation of the MRI scanner.
40 million
The estimated number of MRI scans performed every year in the U.S.
Source: bannerhealth.com, “First MRI? Here Is What to Expect,” July 6, 2020
“The technologist in Charleston can actually run the MRI scanner if need be, and usually does,” Munden adds.
This setup is particularly useful for hospitals in underserved areas, he says, where technologists might perform only a few cardiac MRIs each month, limiting their ability to build specialized skills. “Without this program, patients would have to drive an hour or two to a site with the necessary expertise,” he adds.
The program not only increases access to advanced MRIs but also helps to spread specialized knowledge across the network.
This extends beyond the borders of the U.S. to countries such as Tanzania, where MUSC is working with a local hospital to bring virtual MRI capabilities to underserved patients there.
“It’s something that would be valuable to many health systems,” he says. “With virtual MRI technology, we can reach patient populations that wouldn’t normally have access to it.”


